Led by Professor Cao Lei, department of Landscape architecture, Tianjin University explores the multidisciplinary collaboration and interaction of environmental science, hydraulic engineering and landscape architecture and engages in landscape planning and design with the numerical simulation method relying on the powerful advantage of discipline group in Tianjin University and Tianjin research and engineering center for ecological landscape technology. After years of effort, Sponge cities planning and landscape ecological restoration technology has become the central character of our department. In this regard, the department got 2nd Prize of Tianjin Excellent Science and Technology Progress in 2017 and 2nd Prize of CHSLA Science and Technology Progress in 2018.
Members of this department host more than 10 items of National Natural Science Fund project, 1 items of China Postdoctoral Science Fund project, and more than 30 items of other provincial and ministerial level scientific and technological projects. Win 1st Prize of Tianjin Excellent Construction Design(2012,2013,2015,2017). Win 2nd Prize of National Education Ministry Award (2014). Win 3rd Prize of National Education Ministry Award (2015).
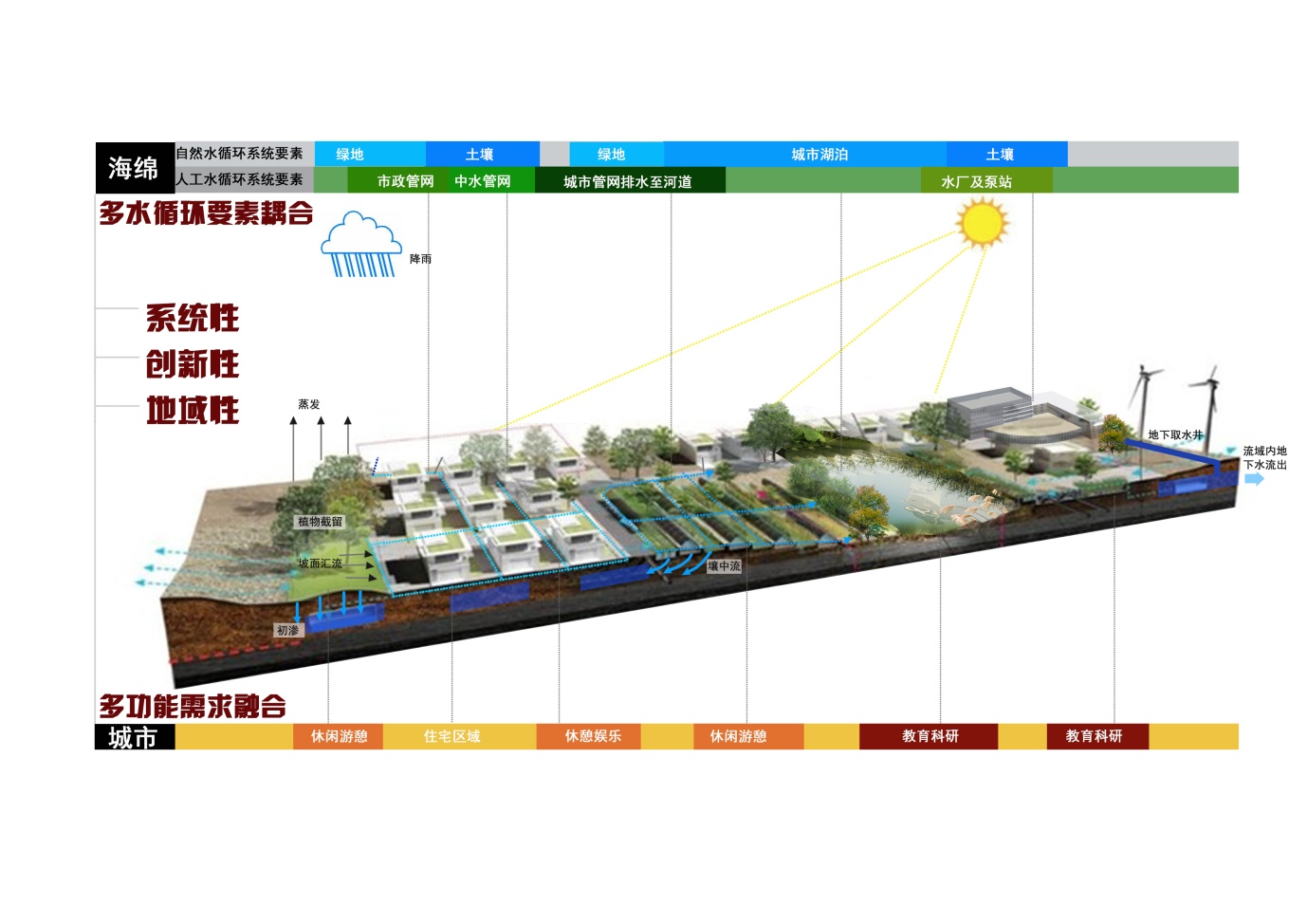
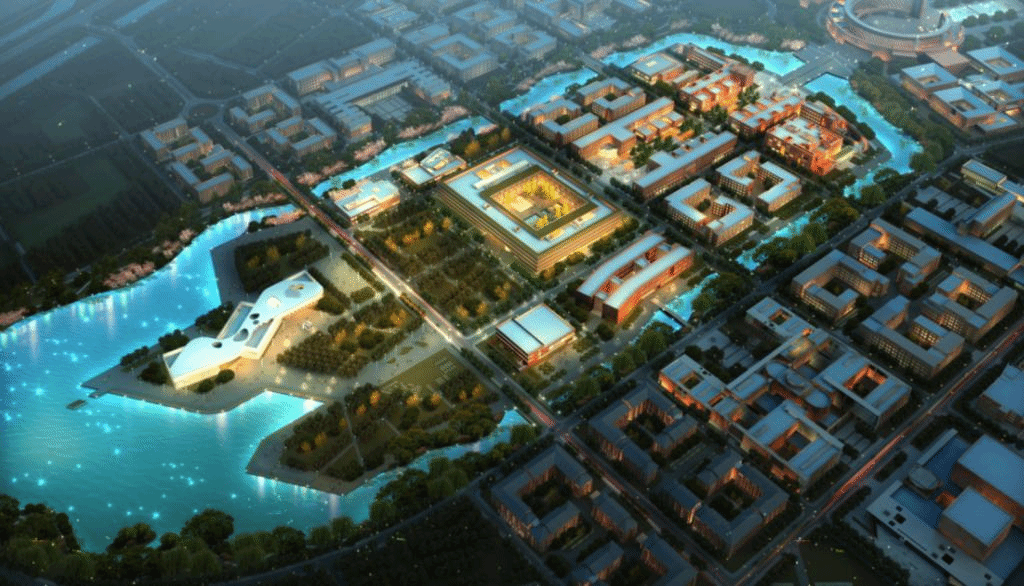
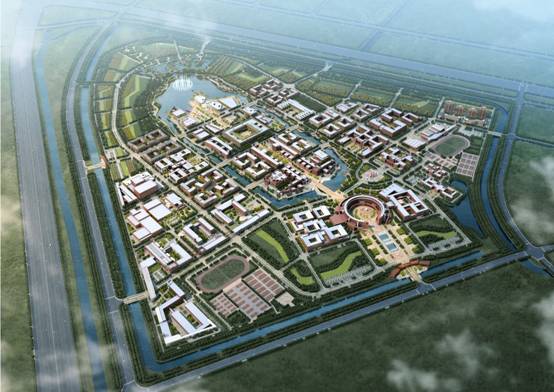
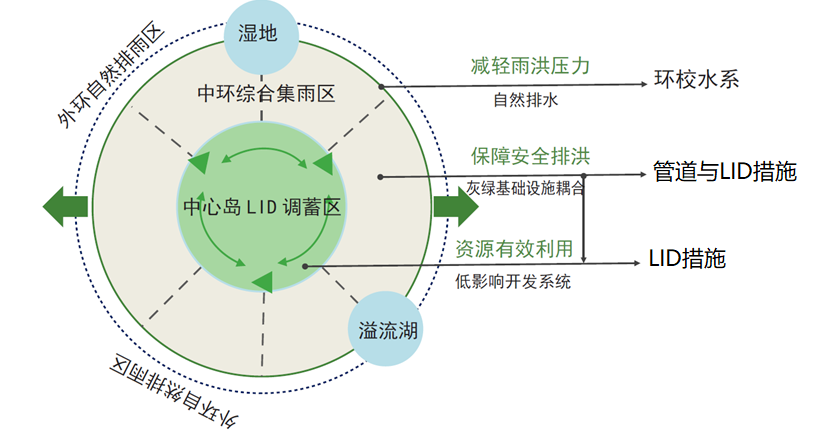
“Landscape planning and design of Tianjin University new campus” holds on the core idea that inheritance the culture gene of this century-aged university and utilization of ecological landscape technologies. In this new campus of 3700 acres, designers not only focus on the inheritance and expression of the culture gene of this century-aged university, but also systematically utilize LID (Low Impact Development) stormwater management technologies in water landscape planning and design. This new campus has been the first exemplication of Sponge city in Tianjin.

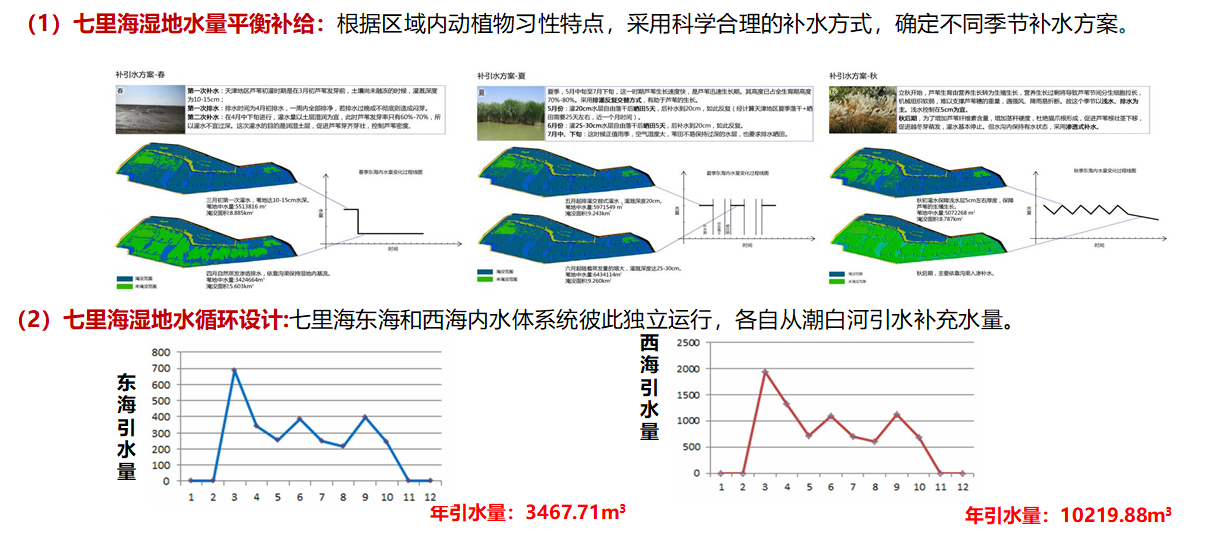
Ecological protection and remediation planning of Qilihai wetland (Tianjin Ancient Seashore and Wetland National Nature Reserve) focuses on the core area in Qilihai with 44.85square kilometer. In view of its unique ancient geological remains and wetland resource, Qilihai wetland become one of the three biggest ancient coast wetlands in the world with ancient shell dike coast in Louisiana St. Louis, U. S. and ancient lagoon wetland in Suriname, South America. This ecological remediation planning is divided into two parts: Qilihai wetland ecological system remediation and ancient geological remains protection which include swamp, bird islands and reed shallows remediation, water system planning, restoration of animal habitat and plant community and so on.